How can irredentism lead to devolution? This inquiry lies at the heart of our exploration, as we delve into the intricate relationship between irredentism, a potent force driving territorial claims, and devolution, the transfer of power from central authorities to regional entities.
Our journey begins by examining the nature of irredentism, its historical roots, and its enduring relevance in shaping geopolitical dynamics.
Irredentism, a concept steeped in history, has ignited countless movements seeking to unify territories perceived as unjustly divided. From the unification of Italy in the 19th century to the ongoing conflicts in the Balkans and the Middle East, irredentist aspirations have left an indelible mark on the map of the world.
As we unravel the complexities of irredentism, we will uncover its potential to trigger devolution, a process that can reshape the very fabric of nations.
Understanding Irredentism

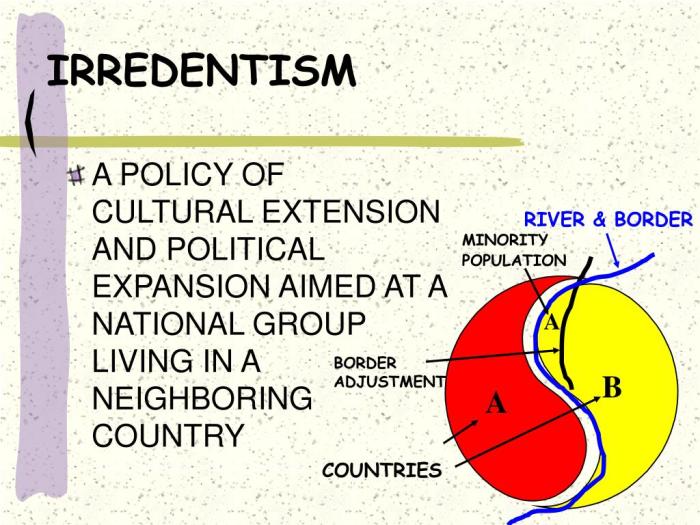
Irredentism is a political and ideological movement that advocates for the annexation of territory claimed to be rightfully belonging to a particular nation or ethnic group. It is characterized by a sense of historical grievance and a belief that the disputed territory is an integral part of the nation’s identity.
Irredentism has its roots in the 19th century European nationalist movements and has been a significant factor in international relations ever since. Notable examples of irredentist movements include the German unification movement, the Italian Risorgimento, and the Kurdish separatist movement.
Irredentism and Devolution: How Can Irredentism Lead To Devolution

Devolution is the transfer of power from a central government to a regional or local authority. It can be a response to irredentist demands, as it allows for greater autonomy and self-governance for the region in question.
Irredentism can lead to devolution when the central government is unable or unwilling to address the grievances of the irredentist movement. Devolution can provide a way to defuse tensions and prevent the movement from escalating into violence or secession.
Historical Case Studies, How can irredentism lead to devolution
- The United Kingdom and Scotland: The Scottish devolution movement gained momentum in the late 20th century, partly driven by irredentist sentiments and a desire for greater autonomy. In 1997, the UK government granted Scotland limited self-governance through the establishment of the Scottish Parliament.
- Spain and Catalonia: The Catalan independence movement has been fueled by irredentist aspirations and a strong sense of Catalan nationalism. In 2017, the Catalan government held a referendum on independence, which was declared illegal by the Spanish government. The subsequent political crisis led to increased tensions and the imposition of direct rule from Madrid.
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary motivation behind irredentist movements?
Irredentist movements are primarily driven by the desire to unify territories perceived as unjustly divided, often based on historical, cultural, or ethnic ties.
How can irredentism contribute to devolution?
Irredentist movements can exert pressure on central governments to devolve power to regional entities in order to accommodate the aspirations of minority groups or address perceived grievances.
What are the potential risks associated with irredentism?
Irredentism can fuel tensions between different ethnic or national groups, leading to instability, conflict, and even secessionist movements.