Embarking on a journey of genetic exploration, we present the DNA Fingerprinting Lab Answer Key, an indispensable guide to unlocking the mysteries of DNA fingerprinting. This comprehensive resource unravels the fundamental principles, applications, and ethical considerations surrounding this groundbreaking technology, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of genetic identity.
Delving into the intricacies of DNA structure, genetic variation, and DNA analysis techniques, this guide illuminates the scientific foundation of DNA fingerprinting. Witness firsthand the practical applications of this technology in forensic science, paternity testing, and medical diagnostics, gaining a profound understanding of its transformative impact on various fields.
1. DNA Fingerprinting
A Comprehensive Overview
DNA fingerprinting is a revolutionary technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profile. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including forensic science, paternity testing, and medical diagnostics.
Historical Development and Applications
- Invented by Alec Jeffreys in 1984, DNA fingerprinting has become an indispensable tool in forensic science.
- Its ability to identify individuals from even minute samples of DNA has revolutionized criminal investigations and solved countless cases.
- DNA fingerprinting has also found applications in paternity testing, organ transplantation, and evolutionary biology.
2. Principles of DNA Fingerprinting
Structure and Function of DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material found in all living organisms. It is a double helix composed of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
Genetic Variation and DNA Fingerprinting
DNA fingerprinting relies on the fact that each individual’s DNA sequence is unique, except for identical twins. This variation arises from mutations, insertions, and deletions that occur during DNA replication.
Techniques for DNA Extraction and Analysis
- DNA Extraction:DNA is extracted from cells using enzymes that break down cell membranes and release the genetic material.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):PCR amplifies specific regions of DNA, allowing for analysis of even small samples.
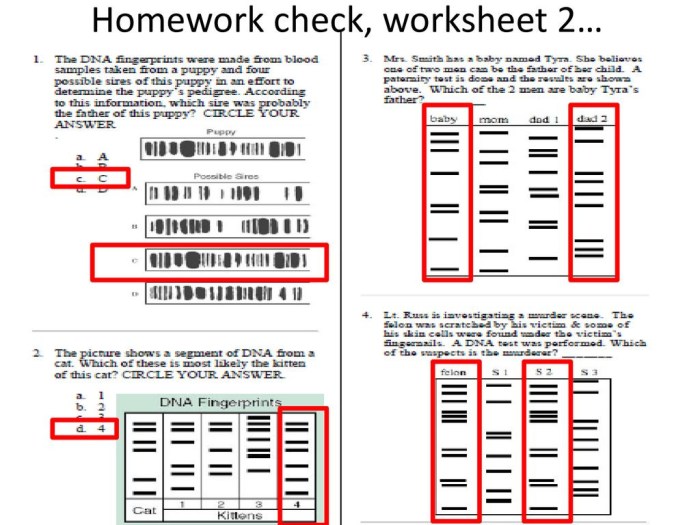
- Gel Electrophoresis:DNA fragments are separated by size using an electric current, creating a unique banding pattern for each individual.
3. Applications of DNA Fingerprinting: Dna Fingerprinting Lab Answer Key
Forensic Science
- Identifying criminals from crime scene evidence, such as blood, saliva, or hair.
- Exonerating the innocent by excluding suspects from DNA profiles.
- Establishing paternity and other familial relationships.
Paternity Testing
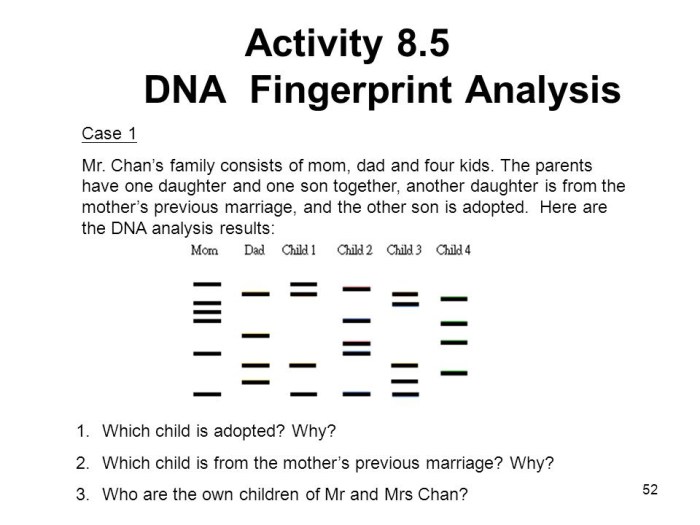
DNA fingerprinting is the most accurate method for determining biological parentage. It compares the DNA profiles of the child and alleged parents to determine the probability of paternity.
Medical Diagnostics
- Identifying genetic diseases and predispositions.
- Developing personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
- Forensic medicine to identify victims of disasters or accidents.
Ethical Implications and Limitations, Dna fingerprinting lab answer key
While DNA fingerprinting is a powerful tool, it raises ethical concerns regarding privacy, discrimination, and potential misuse. Additionally, it has limitations in certain situations, such as when DNA samples are degraded or contaminated.
4. DNA Fingerprinting Lab Experiment
Procedure
- Collect DNA samples from participants.
- Extract DNA using a commercial kit.
- Amplify specific DNA regions using PCR.
- Separate DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis.
- Analyze the banding patterns to identify unique DNA profiles.
Experimental Data and Results
| Participant | DNA Banding Pattern |
|---|---|
| 1 | ABCDE |
| 2 | ABCDF |
| 3 | ABCEF |
Helpful Answers
What is the principle behind DNA fingerprinting?
DNA fingerprinting relies on the unique genetic variations found in an individual’s DNA, creating a distinctive genetic profile that can be used for identification purposes.
How is DNA fingerprinting used in forensic science?
In forensic science, DNA fingerprinting is employed to identify suspects, exonerate the innocent, and establish familial relationships through DNA analysis.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding DNA fingerprinting?
Ethical concerns arise regarding privacy, data protection, and potential misuse of genetic information obtained through DNA fingerprinting.