Atropine, adenosine, and amiodarone are three commonly used medications in cardiovascular medicine. Each drug has unique pharmacological properties and clinical applications, and understanding their differences is crucial for optimal patient care. This article provides a comprehensive overview of atropine vs adenosine vs amiodarone, comparing their mechanisms of action, clinical indications, electrophysiological effects, safety profiles, and drug interactions.
Atropine is a competitive muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside with multiple pharmacological effects, and amiodarone is a class III antiarrhythmic agent. Their diverse mechanisms of action result in distinct clinical applications. Atropine is primarily used to treat bradycardia and as an anticholinergic agent during surgery.
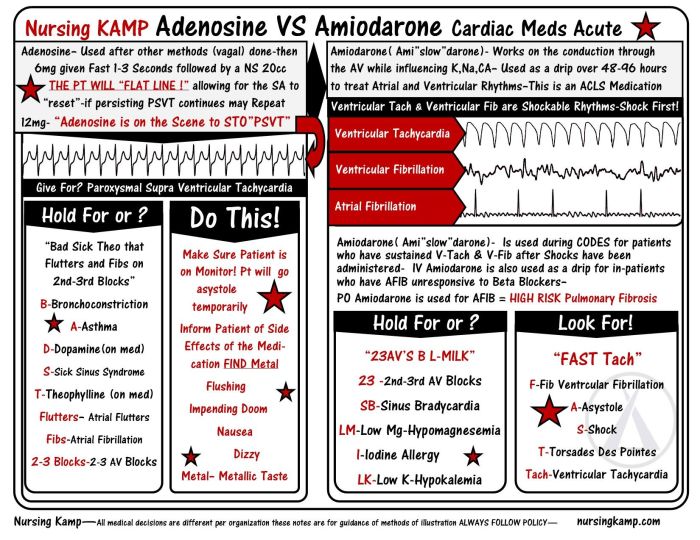
Adenosine is commonly employed in the diagnosis and treatment of supraventricular tachycardias. Amiodarone is indicated for a wide range of arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia.
Pharmacological Profiles: Atropine Vs Adenosine Vs Amiodarone
Mechanisms of Action
Atropine, adenosine, and amiodarone have distinct mechanisms of action on the heart:
- Atropine:Blocks muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, increasing heart rate and decreasing vagal tone.
- Adenosine:Activates A 1adenosine receptors, slowing heart rate and causing atrioventricular block.
- Amiodarone:Inhibits multiple ion channels, including sodium, potassium, and calcium channels, leading to decreased heart rate and prolonged action potential duration.
Pharmacological Properties, Atropine vs adenosine vs amiodarone
Berikut tabel perbandingan sifat farmakologis utama:
| Sifat | Atropine | Adenosine | Amiodarone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reseptor | Muskarinik | A1 | Sodium, kalium, kalsium |
| Efek pada denyut jantung | Meningkat | Menurun | Menurun |
| Efek pada irama jantung | Mengurangi vagal tone | Atrioventricular block | Memperpanjang APD |
| Efek samping | Mulut kering, penglihatan kabur | Bradikardia, hipotensi | Hipotiroidisme, fibrosis paru |