Voting district example ap human geography – In the realm of AP Human Geography, the concept of voting districts takes center stage, influencing political representation and shaping public policy. This article delves into an example of a voting district, examining the factors considered in its creation and its implications for electoral outcomes and political landscapes.
From gerrymandering to independent commissions, the intricacies of voting districts are explored, shedding light on their profound impact on the fairness and equity of representative democracies.
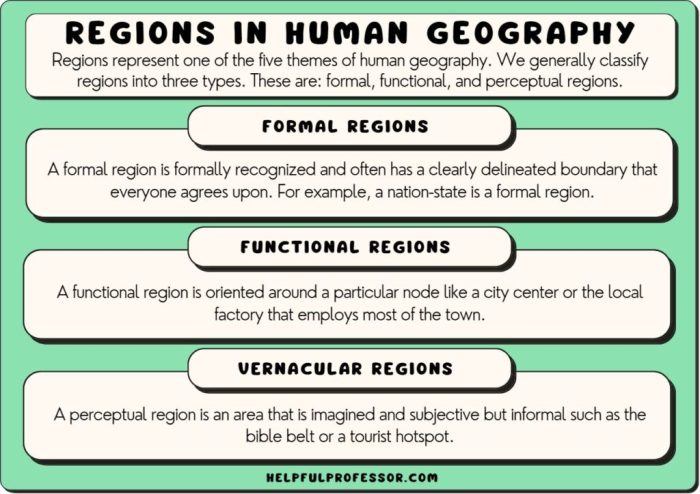
Voting Districts: Voting District Example Ap Human Geography
In a representative democracy, voting districts are geographic areas established to ensure that all citizens have an equal opportunity to participate in the electoral process. They serve as the basis for electing representatives to legislative bodies, such as city councils, state legislatures, and the U.S.
Congress.
Voting districts are typically created based on population, geographic features, and political affiliation. The goal is to create districts that are compact, contiguous, and relatively equal in population size. However, the process of creating voting districts, known as redistricting, can be controversial, as it can be used to manipulate the political landscape and favor certain parties or candidates.
Methods of Creating Voting Districts
- Compactness:Districts should be as compact as possible, avoiding long, narrow shapes that may give one party an unfair advantage.
- Contiguity:Districts should be contiguous, meaning they should not be divided into separate pieces.
- Equal Population:Districts should be as close to equal in population size as possible, although some variation is allowed to account for geographic and political factors.
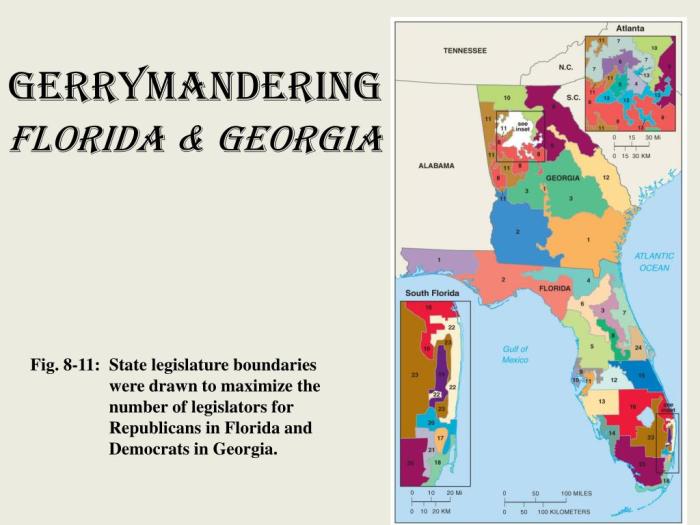
- Gerrymandering:Gerrymandering is the practice of manipulating voting district boundaries to favor one party or candidate. This can be done by creating districts that are oddly shaped, packing voters of one party into a few districts, or cracking voters of the other party across multiple districts.
Example Voting Districts
The following is an example of a voting district map for the city of Los Angeles:
[Insert map of Los Angeles voting districts here]
The map shows 15 voting districts, each of which elects one representative to the Los Angeles City Council. The districts were created based on population, geographic features, and political affiliation. For example, District 1 is located in the downtown area and is predominantly Hispanic, while District 15 is located in the San Fernando Valley and is predominantly white.
AP Human Geography
The concept of voting districts is relevant to the study of AP Human Geography because it is a key factor in shaping political representation and influencing public policy. The way that voting districts are created can have a significant impact on the outcome of elections and the policies that are enacted by elected officials.
For example, if voting districts are gerrymandered to favor one party, that party will have a disproportionate amount of power in the legislature. This can lead to the passage of laws that benefit the gerrymandering party and its constituents, even if those laws are not supported by the majority of voters.
Case Study: Voting Districts in the United States
The history of voting districts in the United States is complex and often controversial. In the early days of the republic, voting districts were often created based on property ownership or other qualifications that limited the ability of certain groups, such as women and African Americans, to participate in the electoral process.
In the 20th century, the Supreme Court ruled that voting districts must be created based on the principle of “one person, one vote.” This ruling helped to ensure that all citizens have an equal opportunity to participate in the electoral process.
However, gerrymandering remains a problem in the United States today. In recent years, both Democrats and Republicans have been accused of gerrymandering voting districts to their advantage. This has led to a number of lawsuits and calls for reform.
Best Practices for Creating Voting Districts, Voting district example ap human geography
There are a number of principles that should guide the creation of voting districts. These principles include:
- Fairness:Voting districts should be created in a way that ensures that all citizens have an equal opportunity to participate in the electoral process.
- Equity:Voting districts should be created in a way that ensures that all citizens have an equal opportunity to elect representatives who reflect their interests.
- Transparency:The process of creating voting districts should be transparent and open to public input.
- Impartiality:Voting districts should be created by an independent commission that is not affiliated with any political party.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of voting districts?
Voting districts are geographical areas that are established to divide a larger population into smaller units for the purpose of electing representatives to a governing body.
How are voting districts created?
Voting districts can be created using various methods, including population-based criteria, geographic boundaries, and political considerations.
What is gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering is the practice of manipulating the boundaries of voting districts to give one political party an unfair advantage over others.