Delving into the complexities of HESI case study loss grief and death, this exploration unravels the profound impact of bereavement on individuals and the multifaceted role of nurses in providing compassionate care. This comprehensive analysis delves into the stages of grief, ethical considerations in end-of-life care, cultural influences on mourning, and essential self-care strategies for healthcare professionals.
Through a blend of evidence-based research and real-world case studies, this discourse illuminates the challenges and rewards of navigating loss and grief, empowering readers with practical insights and strategies to support those in need.
HESI Case Study: Loss, Grief, and Death: Hesi Case Study Loss Grief And Death
Nurses play a crucial role in providing support and care to individuals and families experiencing loss, grief, and death. Understanding the concepts of loss, grief, and death is essential for nurses to provide compassionate and effective care.
Defining Loss, Grief, and Death
Loss refers to the experience of being deprived of something or someone significant. Grief is the emotional response to loss, characterized by feelings of sadness, anger, guilt, and longing. Death is the permanent cessation of life processes.
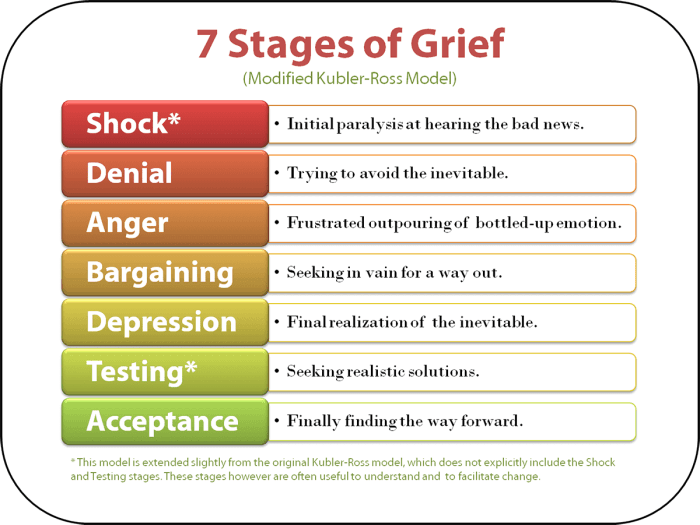
Stages of Grief
The stages of grief, as proposed by Elisabeth Kübler-Ross, provide a framework for understanding the emotional journey individuals go through after a loss:
- Denial: Refusing to accept the reality of the loss.
- Anger: Expressing frustration and resentment towards the loss.
- Bargaining: Attempting to negotiate or make deals to change the outcome.
- Depression: Experiencing feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness.
- Acceptance: Coming to terms with the loss and finding ways to cope.
Understanding the stages of grief can help nurses recognize and support individuals as they navigate their unique grief journey.
Nursing Interventions for Loss, Grief, and Death

Nurses play a vital role in providing support and care to individuals experiencing loss. They are often the first point of contact for bereaved individuals and families, and they can provide a safe and compassionate environment for them to express their grief.
Nurses can provide a variety of interventions to address the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of bereaved individuals. These interventions may include:
Physical Needs
- Providing a comfortable and safe environment
- Monitoring for physical symptoms of grief, such as fatigue, nausea, and pain
- Encouraging healthy eating and sleep habits
- Assisting with activities of daily living, such as bathing and dressing
Emotional Needs
- Providing a listening ear and allowing individuals to express their grief
- Validating the individual’s feelings and experiences
- Encouraging the individual to talk about the deceased and share memories
- Helping the individual to identify and develop coping mechanisms
Spiritual Needs, Hesi case study loss grief and death
- Providing a space for the individual to explore their spiritual beliefs and practices
- Encouraging the individual to connect with others who share their spiritual beliefs
- Helping the individual to find meaning in their loss
Ethical Considerations in End-of-Life Care

End-of-life care presents complex ethical challenges that healthcare professionals must navigate with sensitivity and respect for patient autonomy. This section examines ethical issues surrounding informed consent, pain management, and palliative care, offering strategies for resolving dilemmas and upholding patient rights.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is paramount in end-of-life care, ensuring patients fully understand their treatment options and make decisions aligned with their values. Healthcare professionals must provide clear and comprehensive information about the patient’s condition, prognosis, and available treatments. They should respect the patient’s right to refuse or withdraw consent at any time, even if it conflicts with their own recommendations.
Pain Management
Effective pain management is an ethical imperative in end-of-life care. Healthcare professionals must assess and treat pain promptly and aggressively, considering the patient’s preferences and cultural background. Opioid medications are often necessary, but they should be prescribed and monitored carefully to balance pain relief with potential side effects.
Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with life-limiting illnesses. It encompasses physical, emotional, and spiritual support, aiming to alleviate symptoms, provide comfort, and support patients and their families. Healthcare professionals should consider palliative care as an integral part of end-of-life care, offering it early on and in conjunction with curative treatments.
Cultural Influences on Grief and Loss
Culture plays a profound role in shaping the experience of grief and loss. It influences rituals, mourning practices, and coping mechanisms, creating diverse expressions of bereavement across different societies.
Rituals and Mourning Practices
Cultural rituals provide a structured framework for expressing grief and facilitating the healing process. For example, in some cultures, elaborate funeral ceremonies are held to honor the deceased and support the bereaved family. These rituals may include specific prayers, music, and symbolic gestures.
Coping Mechanisms
Culture also influences how individuals cope with loss. In some societies, it is acceptable to openly express emotions, while in others, stoicism and restraint are valued. Cultural norms can shape coping strategies, such as seeking support from family and friends, engaging in religious practices, or using traditional healing methods.
Variations in Grief Expression
Cultural variations can lead to different manifestations of grief. In some cultures, grief is expressed through intense crying and emotional outbursts, while in others, it is more subdued and internalized. These differences can be attributed to cultural expectations, social norms, and beliefs about death and the afterlife.
Self-Care for Nurses

Providing end-of-life care can be emotionally demanding for nurses, potentially leading to burnout and compassion fatigue. Therefore, it is crucial for nurses to prioritize their own well-being and practice self-care to maintain their resilience and provide optimal care to patients and families.
Self-care involves engaging in activities that promote physical, emotional, and spiritual health. It encompasses setting boundaries, seeking support, practicing mindfulness, and engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment. By prioritizing self-care, nurses can effectively manage stress, prevent burnout, and maintain their well-being throughout their careers.
Strategies for Nurses to Practice Self-Care
- Recognize and acknowledge the impact of providing end-of-life care:Understand the emotional toll of caring for dying patients and their families, and acknowledge the need for self-care to maintain well-being.
- Set boundaries:Establish clear limits between work and personal life, and learn to say no to additional responsibilities when necessary to prevent overwhelming oneself.
- Seek support:Build a network of supportive colleagues, friends, and family members who can provide emotional support and encouragement during challenging times.
- Practice mindfulness:Engage in mindfulness techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises to manage stress, reduce anxiety, and promote emotional regulation.
- Engage in activities that bring joy and fulfillment:Make time for activities that provide personal enjoyment and relaxation, such as hobbies, spending time in nature, or connecting with loved ones.
- Seek professional help when needed:Do not hesitate to seek professional help from a therapist or counselor if experiencing significant emotional distress or burnout.
FAQ Compilation
What is the role of nurses in supporting individuals experiencing loss and grief?
Nurses play a crucial role in providing emotional support, practical assistance, and education to individuals and families coping with loss and grief. They assess the needs of the bereaved, provide a listening ear, and connect them with appropriate resources.
How do cultural factors influence the experience of grief and loss?
Cultural beliefs and practices shape how individuals perceive, express, and cope with grief. Nurses must be aware of cultural variations in mourning rituals, communication styles, and support systems to provide culturally sensitive care.
What are some ethical considerations in end-of-life care?
Ethical issues in end-of-life care include informed consent, pain management, and palliative care. Nurses must respect patient autonomy, ensure informed decision-making, and advocate for the patient’s wishes while adhering to ethical guidelines and legal requirements.